In today's data-driven world, the need for real-time processing and faster decision-making is paramount. Edge computing has emerged as a revolutionary technology, designed to bring data storage and processing closer to where it's generated—right at the "edge" of the network. But what exactly does edge computing mean, and how does it impact our digital landscape? Let’s dive deep into the world of edge computing.
How Edge Computing Differs from Cloud Computing
To understand edge computing, we must first compare it to cloud computing, which has been the dominant model for years. Cloud computing stores and processes data in centralized data centers, often located far from where data is generated. This can result in delays (latency), especially for real-time applications.
Edge computing, on the other hand, processes data closer to its source, often directly on edge devices or at local data centers. This decentralization reduces the time needed to process data and reduces bandwidth use.
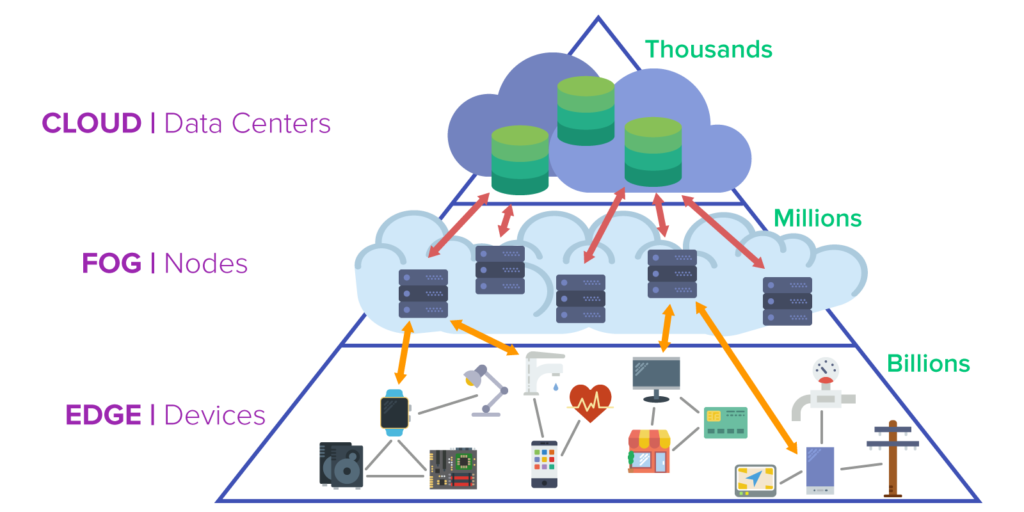
Key Differences Between Edge and Cloud Computing:
- Data Location: Cloud computing centralizes data processing, while edge computing decentralizes it to local nodes.
- Latency: Edge computing significantly reduces latency, which is critical for real-time tasks.
- Bandwidth: By processing data locally, edge computing minimizes the amount of data sent to the cloud, lowering bandwidth costs.
- Scalability: Cloud computing is more scalable since it has vast resources, whereas edge computing focuses on localized processing.
The Growing Importance of Real-Time Data Processing
In a world where milliseconds matter, real-time data processing has become increasingly vital. Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and autonomous vehicles rely on split-second decisions. For instance, in autonomous vehicles, a slight delay in processing could mean the difference between safety and disaster.
Edge computing ensures that real-time analytics happen as close to the source as possible, providing faster insights, instant decision-making, and a more seamless user experience.
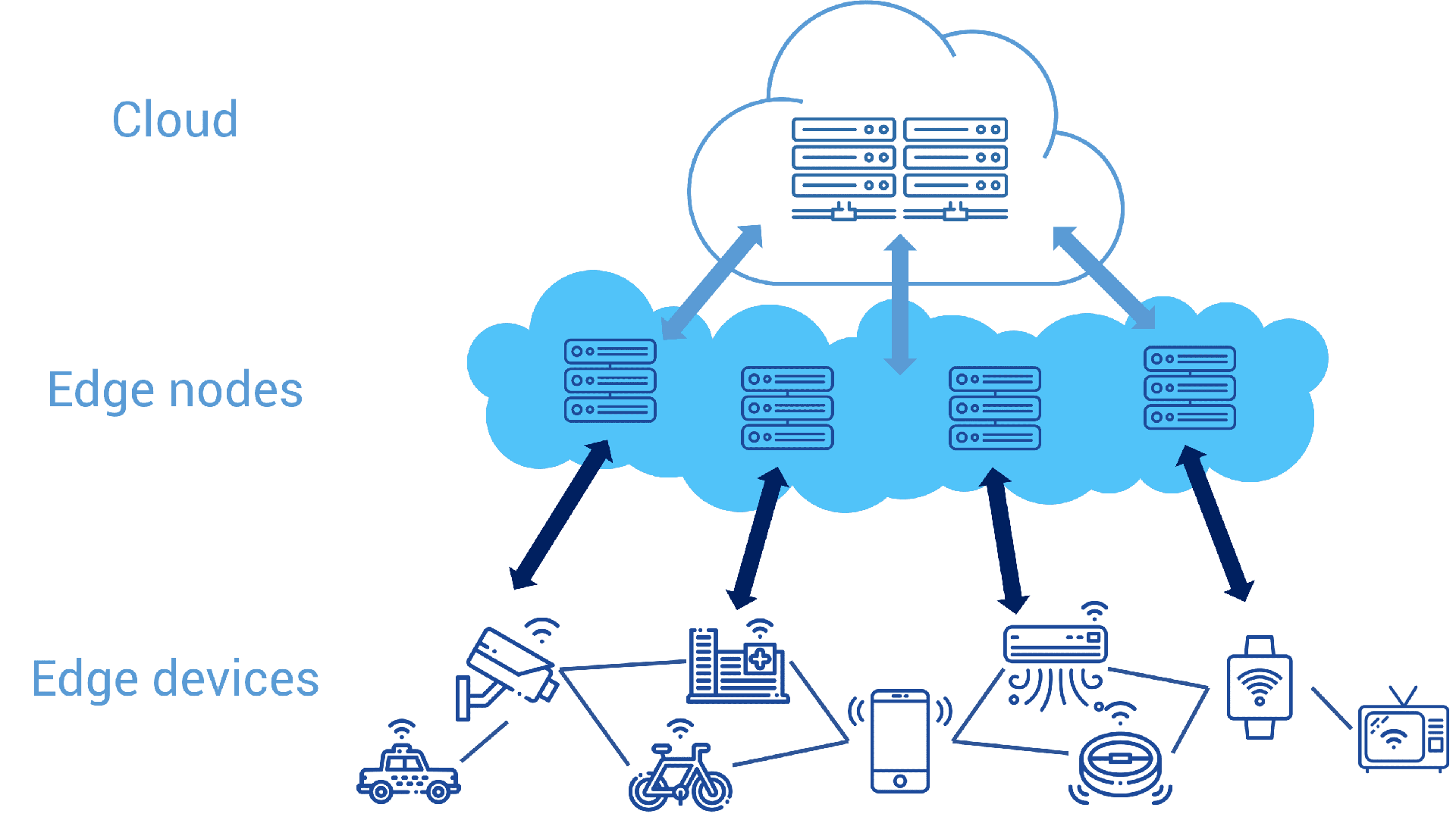
Core Components of Edge Computing
Edge computing is made up of several essential components:
- Edge Devices: These are physical devices like sensors, cameras, or IoT (Internet of Things) gadgets that gather data.
- Edge Gateways: These act as intermediaries, managing and processing data between edge devices and the cloud or local data centers.
- Localized Data Centers: Small-scale data centers that handle a significant portion of data processing locally, reducing the need for cloud involvement.
How Edge Computing Works: A Simplified Explanation
At its core, edge computing brings data processing closer to the end-user. Rather than sending all data to a remote cloud for processing, edge devices and gateways handle data locally. This reduces the time (latency) it takes for data to travel back and forth.
For example, think of smart security cameras. Instead of sending hours of footage to the cloud, edge computing allows the camera to process footage locally and only send relevant events (like motion detection) to the cloud. This reduces both bandwidth use and processing delays.
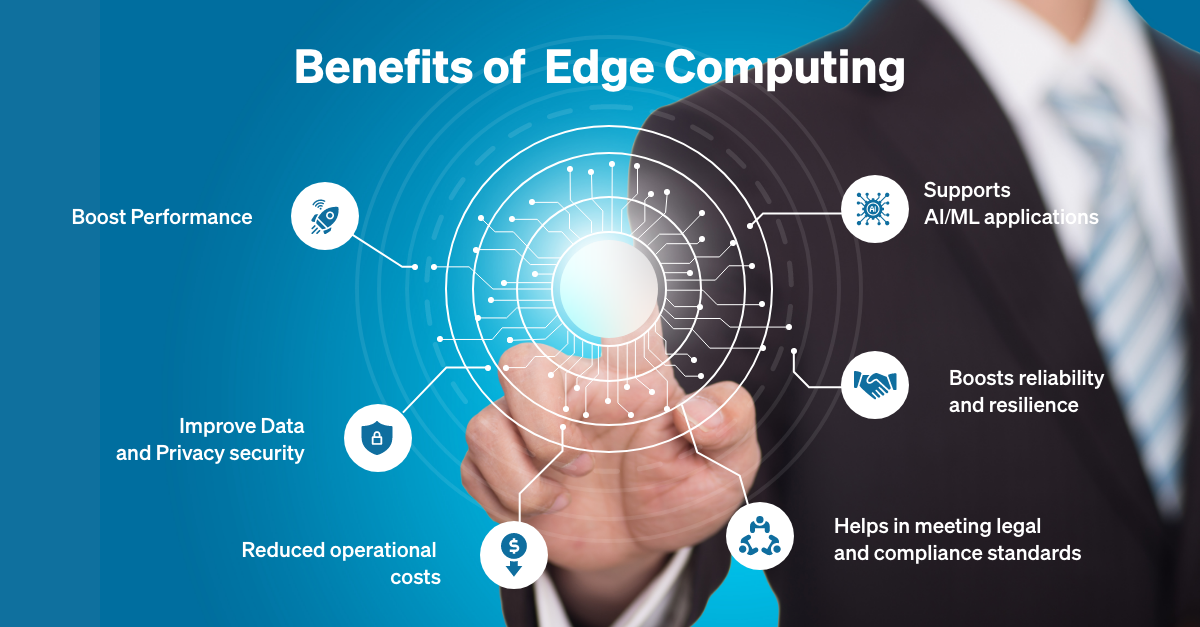
Advantages of Edge Computing
1. Reduced Latency and Faster Processing
By keeping data closer to the source, edge computing minimizes the lag between data generation and processing, enabling faster decision-making.
2. Enhanced Security and Privacy
Processing data locally means less sensitive information is sent to the cloud. This reduces exposure to cyber-attacks and enhances privacy.
3. Lower Bandwidth Costs
Since edge computing reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud, it can significantly lower bandwidth costs, especially in data-heavy applications like video streaming or IoT.
4. Improved Reliability and Resilience
Edge computing can continue functioning even if the cloud is down, ensuring continuous service. This makes it more reliable in remote areas or environments with intermittent internet connectivity.
Challenges and Limitations of Edge Computing
Despite its benefits, edge computing has some challenges:
- Scalability: Managing multiple distributed edge nodes can be more complex than relying on a centralized cloud system.
- Security: While edge computing can improve privacy, it also presents security challenges, as each edge node must be adequately protected.
- Distributed Infrastructure: The management of decentralized systems adds complexity and operational overhead.
Use Cases of Edge Computing Across Different Industries
1. Healthcare
Edge computing supports real-time diagnostics and remote monitoring of patients, allowing doctors to access patient data faster.
2. Manufacturing
Edge-powered predictive maintenance helps detect potential equipment failures in real-time, reducing downtime and optimizing production efficiency.
3. Transportation
Autonomous vehicles rely on edge computing to process massive amounts of sensor data instantly, allowing for safe and responsive navigation.
4. Retail
Edge computing helps retailers offer enhanced shopping experiences by providing real-time inventory updates and personalized promotions.
5. Smart Cities
Edge computing plays a crucial role in the development of smart cities, enabling real-time traffic management, energy consumption monitoring, and public safety applications.
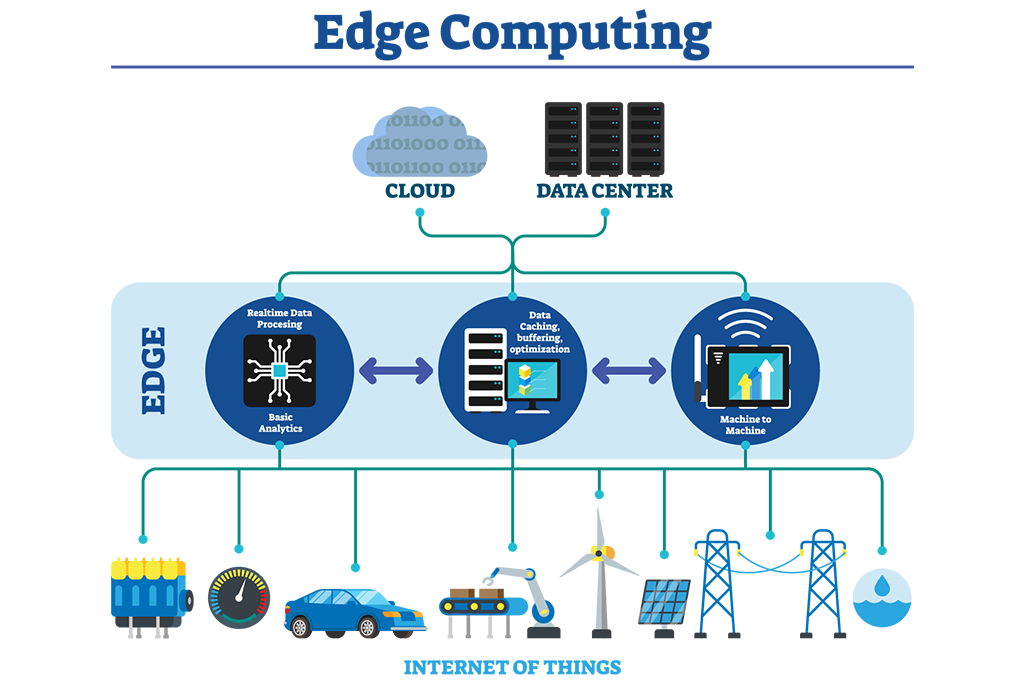
Edge Computing in IoT (Internet of Things)
The IoT revolution has led to an explosion of connected devices, all generating massive amounts of data. Edge computing helps process this data locally, reducing the load on central cloud systems. By doing so, it allows IoT devices to function efficiently even with limited internet connectivity.
Security and Privacy Concerns in Edge Computing
With data being processed at the edge, security risks shift to local devices and gateways. Ensuring that edge nodes are secure and that data is encrypted both at rest and in transit is critical. Companies must also ensure data integrity across all distributed systems to prevent vulnerabilities.
Future of Edge Computing
The future of edge computing looks promising, especially with the rise of 5G networks, which will further reduce latency and enable even faster data processing at the edge. As more businesses and industries adopt edge technology, we’ll see a push towards integrating it with AI, IoT, and other cutting-edge innovations.
Edge Computing vs. Fog Computing
Though often used interchangeably, edge computing and fog computing have key differences. Fog computing extends the cloud closer to the edge by processing data across multiple points (both at the edge and in cloud servers), while edge computing keeps processing entirely local.

The Role of Edge Computing in 5G Networks
5G technology promises faster speeds and reduced latency, making it the perfect complement to edge computing. Together, they will enable advancements in areas like autonomous driving, telemedicine, and smart city infrastructures.
Edge Computing and AI: A Powerful Combination
With AI now being deployed at the edge, we see intelligent decision-making happening right at the source. Examples include smart home systems, factory robots, and AI-powered cameras.
Edge computing is fundamentally reshaping how we process and analyze data. With its ability to deliver faster insights, improve security, and lower costs, it’s no surprise that more industries are adopting edge solutions. As technology continues to advance, edge computing will play an even more significant role in our connected world, enabling smarter devices, smarter cities, and smarter industries.
FAQs
1. What is edge computing in simple terms?
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency
and improving speed by minimizing reliance on centralized cloud systems.
2. How does edge computing benefit businesses?
Businesses benefit from faster data processing, improved security, reduced
bandwidth costs, and increased reliability.
3. What industries are adopting edge computing the most?
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, retail, transportation, and
smart cities are leading in edge computing adoption.
4. How does edge computing support IoT devices?
Edge computing processes data locally, reducing the need for IoT devices
to send vast amounts of data to the cloud, improving efficiency.
5. What are the security risks of edge computing?
Security risks include vulnerabilities at edge nodes, which can be mitigated by encryption, secure networks, and proper infrastructure management.
Edge Computing: Revolutionizing Real-Time Data Processing